Landlords and tenants will face legal issues during the rental process, but not every issue needs to involve the courts. This article will help you learn how the laws in your state handle everything from security deposits to termination notices so you can easily navigate these.
This article is not an exhaustive or a substitute for qualified legal advice. Laws and statutes are subject to change and may vary by county or city. You are responsible for performing your research and complying with all laws applicable to your unique situation.
We recommend consulting with the appropriate government agencies and a qualified lawyer if you have legal questions or concerns. Your state bar association may have a referral service to help you find a lawyer with experience in landlord-tenant law.
Official Rules and Regulations
- S.D. Codified Laws Ann. §§ 43-32-1 to 43-32-30 – Lease of Real Property
- S.D. Codified Laws Ann. §§ 15-2-1 to 15-2-36 – Limitation of Actions Generally
- S.D. Codified Laws Ann. §§ 21-16-1 to 21-16-12 – Forcible Entry and Detainer
- Landlord/Tenant–Consumer Protection, South Dakota Attorney General
Security Deposit:
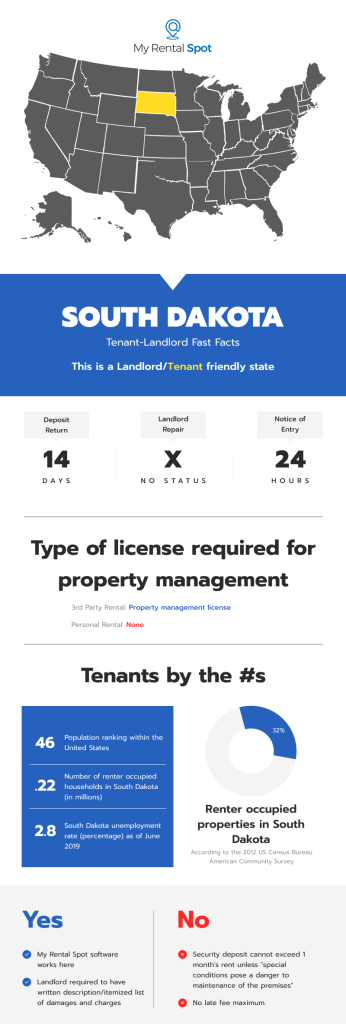
- Security Deposit Maximum: One month’s rent, but a more significant amount may be agreed to in the lease “where special conditions pose a danger to the maintenance of the premises” (§§ 43-32-6.1).
- Security Deposit Interest: No statute.
- Separate Security Deposit Bank Account: No statute.
- Pet Deposits: No statute.
- Non-Refundable Fees: No statute
- Deadline for Returning Security Deposit: A written statement of any withholdings must be given within two weeks, but the landlord has 45 days to provide an itemized list of damages, and the tenant must request it. (§§ 43-32-24)
- Permitted Uses of the Deposit:
- To cover unpaid rent or other funds due under the lease;
- To restore the premises to the conditions at the start of the tenancy, except for ordinary wear and tear. (§§ 43-32-24)
- Require Written Description/Itemized List of Damages and Charges: Required if requested, and the landlord has 45 days from the termination date to provide it. (§§ 43-32-24)
- Record Keeping of Deposit Withholdings: No statute.
- Receipt of Deposit: No law.
- Failure to Comply: A landlord who fails to comply with §§ 43-32-24 forfeits the right to withhold any portion of the deposit. Bad faith retention of any part of a deposit, including failure to provide the written statement and itemized list of damages, subjects the landlord to punitive damages of up to $200 (§§ 43-32-24).
Lease, Rent & Fees:
- Rent Is Due: Rent is due in month-long increments at the end of each month (§§ 43-32-12).
- Rent Increase Notice: A 30-day written notice is required (§§ 43-32-13).
- Rent Grace Period: No statute.
- Late Fees: No statute. Any provision for charging late fees must be specified in the lease.
- Prepaid Rent: No statute.
- She returned Check Fees: $40. The statute requires notice of the returned check fee policy to be conspicuously posted or provided in a written statement. (§§ 57A-3-421)
- Tenant Allowed to Withhold Rent for Failure to Provide Essential Services (Water, Heat, etc.): Statute doesn’t specifically allow withholding rent for failure to provide essential services but does allow for withholding rent when there are conditions that make the premises unfit for habitation, with written notice and giving the landlord reasonable time to remedy. (§§ 43-32-9)
- Tenant Allowed to Repair and Deduct Rent: Yes. Tenant must first give written notice specifying conditions that require repair to make the premises fit for habitation. If the landlord doesn’t repair within a reasonable amount of time, the tenant can repair and deduct the cost from the rent. For repairs requiring more than one month’s rent, the the tenant may, after giving written notice specifying the reason, withhold the rent, deposit it in a separate bank account, and give the landlord written proof of each deposit. If the landlord repairs, the tenant must release the withheld rent to the landlord. If the repair hasn’t been done, and enough money has been paid into the account for the repair to be done, the tenant may pay for the repair from the account. (§§ 43-32-9)
- Landlord Allowed to Recover Court and Attorney Fees: No statute.
- The landlord must make a reasonable attempt to mitigate damages to the lessee, including an effort to Rent: No statute.
- Abandonment/Early Termination Fee: No statute.
Notices and Entry:
- Notice to Terminate Tenancy – Fixed End Date in Lease: Notice is not required, as the lease terminates on the date agreed to in the lease (§§ 43-32-22(1)).
- Notice to Terminate Tenancy – Yearly Lease with No End Date: Any rental agreement for longer than a year must be agreed to in writing. (§§ 43-32-5)
- Notice to Terminate Tenancy – Month-to-Month Lease: 30-day written notice required. The tenant may give notice to terminate the lease effective the first day of the next month within 15 days of receiving notice of a modification to the lease from the landlord. Tenants at will who are active military service members and their immediate family are entitled to two months’ written notice. See §§ 43-8-8 for restrictions. (§§ 43-32-13 and §§ 43-8-8)
- Notice to Terminate Tenancy – Week-to-Week Lease: If no end date is specified in the agreement, a one-week notice is required to terminate (§§ 43-32-15).
- Termination of Tenancy with 24 Hours Notice: Landlords may start the eviction process immediately and without notice if the tenant “commits waste” upon the premises or does or fails to do anything that is grounds for termination under the lease (§§ 21-16-1(7)).
- Notice of Date/Time of Move-Out Inspection: No statute.
- Notice of Termination of Week-to-Week Leases for Nonpayment: Rent is due at the end of the period for lease periods shorter than a month. Landlords can start eviction if rent is three days past due (§§ 43-32-12 and §§ 21-16-1(4)).
- Notice of Termination of All Other Leases for Nonpayment: Landlords may start eviction if rent is three days past due (§§ 21-16-1(4)).
- ●ermination for Lease Violation: Landlords may terminate the lease before the end of the term if the tenant allows the premises to be used in a way that violates the lease or if the tenant doesn’t make any requested repairs for which the tenant is responsible for making (§§ 43-32-18).
- Required Notice before Entry: Reasonable notice of at least 24 hours is required in writing, specifying the reason for entry, the date or dates and time of access during business hours, and providing the tenant an opportunity to reschedule (§§ 43-32-32).
- Entry Allowed with Notice for Maintenance and Repairs (non-emergency): Reasonable notice of at least 24 hours required in writing, specifying the reason for admission, the date or dates and time of access during business hours, and providing the tenant an opportunity to reschedule (§§ 43-32-32).
- Entry Allowed with Notice for Showings: Reasonable notice of at least 24 hours required in writing, specifying the reason for admission, the date or dates and time of entry during business hours, and providing the tenant an opportunity to reschedule (§§ 43-32-32).
- Emergency Entry Allowed without Notice: Notice not required in cases of emergency (§§ 43-32-32).
- Entry Allowed During Tenant’s Extended Absence: No statute.
- Notice to Tenants for Pesticide Use: No statute.
- Lockouts Allowed: No (§§ 43-32-6).
- Utility Shut-offs Allowed: No (§§ 43-32-6).
Disclosures and Miscellaneous Notes:
- Name and Addresses: No statute.
- Copy of the Lease: No statute.
- Domestic Violence Situations: No statute.
- Landlord’s Duties: (§§ 43-32-8)
- Repairs and Habitability: Keep the premises and all common areas in reasonable repair and fit for human habitation and in good and safe working order, except when the disrepair was caused by tenant action or negligence.
- Maintenance: Maintain in good and safe working order and condition all electrical, plumbing, or heating systems of the premises, except when the disrepair has been caused by tenant action or negligence.
- Tenant’s Duties: (§§ 43-32-10)
- Preserve and Repair: Preserve the premises and appliances in good condition, and repair all damage caused by the tenant’s negligence or actions or that caused by anyone on the property under the tenant’s control.
- Retaliation: Landlord must not terminate or refuse to renew a lease to a tenant who has filed an official complaint to a government agency, or has been involved in a tenant’s organization. Other actions are prohibited. Read §§ 43-32-27 and §§ 43-32-28 for more information.
- Lead Disclosure: Landlords must disclose all known lead paint hazards. Landlords must also provide tenants, as an attachment to a written lease, with an information pamphlet on lead-based paint hazards.
- Disclosure of Knowledge of Prior Manufacturing of Methamphetamine: If a landlord knows that the premises have been used to manufacture methamphetamine, they must disclose that knowledge to the tenant or prospective tenant. If the premises consist of two or more housing units, the disclosure requirement applies only to the unit where it is known that methamphetamine was manufactured (§§ 43-32-30).
- Abandoned Property: Any property left on the premises by the tenant of less than $500 in value for more than 10 days may be considered abandoned and disposed of by the landlord. If the value of property left on the premises is greater than $500, then the landlord must store if for up to 30 days, after which they may dispose of the abandoned property (§§ 43-32-25 and §§ 43-32-26).
Court Related:
- South Dakota Small Claims Court
- Limits: $12,000. However, this limit may change from time to time, so the South Dakota Unified Judicial System suggests that the person seeking to file a small claim first verify with the clerk of the court the maximum amount that can be claimed. (§ 16-12C-13)
- Eviction Cases Allowed in Small Claims: No, eviction cases are heard in a circuit court or magistrate court presided over by a magistrate judge. (§ 21-16-3)
- Guide to Small Claims Court in South Dakota (PDF)
- Statute of Limitations
- Written Contracts: 6 years (§§ 15-2-13(1)).
- Oral Contracts: 6 years (§§ 15-2-13(1)).
- South Dakota Unified Judicial System
- South Dakota Attorney General
- State Bar of South Dakota
- Legal Aid:
Business Licenses:
- Business License Required: No statewide statute, but local cities and counties may have regulations and requirements. Check with your local governing authority.
Helpful Links
State Agencies & Regulatory Bodies
- U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development – South Dakota
- South Dakota Insurance Division
- South Dakota Consumer Protection
- South Dakota Consumer Handbook (PDF)
- South Dakota Real Estate Commission
Housing Authorities
- South Dakota Housing Development Authority
- Pennington County Housing and Redevelopment Commission
- Sioux Falls Housing
Realtor and Landlord Associations
- REALTORS® Associations
- South Dakota Association of REALTORS®
- REALTOR® Association of the Sioux Empire
- Black Hills Association of REALTORS®
- Aberdeen Area Association of REALTORS®
- Central South Dakota Board of REALTORS®
- East Central Board of REALTORS®
- Huron Board of REALTORS®
- Meridian Association of REALTORS®
- Mitchell Board of REALTORS®
- Mount Rushmore Area Association of REALTORS®
- Northeast South Dakota Association of REALTORS®
- Landlord Associations
