Landlords and tenants will face legal issues during the rental process, but not every issue needs to involve the courts. This article will help you learn how the laws in your state handle everything from security deposits to termination notices so you can easily navigate these.
This article is not an exhaustive or a substitute for qualified legal advice. Laws and statutes are subject to change and may vary by county or city. You are responsible for performing your research and complying with all laws applicable to your unique situation.
We recommend consulting with the appropriate government agencies and a qualified lawyer if you have legal questions or concerns. Your state bar association may have a referral service to help you find a lawyer with experience in landlord-tenant law.
Official Rules and Regulations
- Ohio Rev. Code Ann. §§ 5321.01 – 5321.19 – Landlords and Tenants
- Ohio Rev. Code Ann. §§ 5323.01 – 5323.99 – Residential Rental Property
- [ GUIDE ] Ohio Tenant-Landlord Law – General Guidelines (PDF)
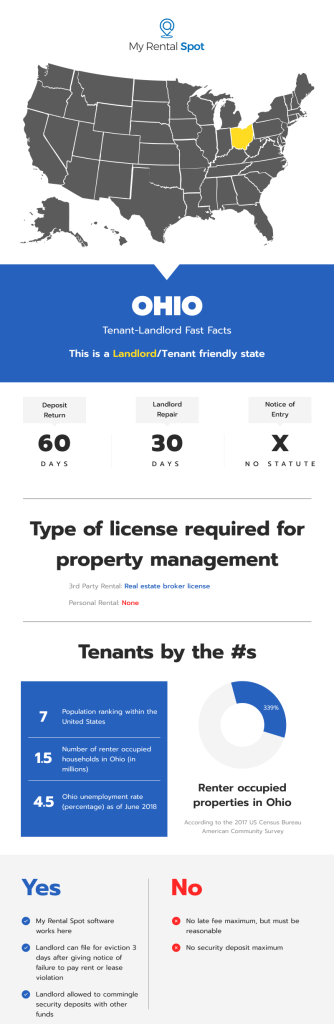
Security Deposit:
- Security Deposit Maximum: No statute.
- Security Deposit Interest: If the tenancy is longer than six months, five percent interest per annum is required to be paid to the Tenant each year on the amount of any deposit that exceeds $50 or one month’s rent, whichever is greater (§§ 5321.16).
- Separate Security Deposit Bank Account: No statute.
- Pet Deposits: No regulation.
- Non-Refundable Fees: No statute.
- Deadline for Returning Security Deposit: 30 days from the time the Tenant moves out (§§ 5321.16(B))
- Permitted Uses of the Deposit: The security deposit can be used to pay for unpaid rent or damages due to the Tenant’s noncompliance with either the rental agreement or statutory tenant obligations (§§ 5321.16(B)).
- Require Written Description/Itemized List of Damages and Charges: Yes (§§ 5321.16(B)).
- Record Keeping of Deposit Withholdings: No statute.
- Receipt of Deposit: No law.
- Failure to Comply: If landlords fail to provide an itemized list of damages, the Tenant may sue to recover the money withheld along with damages equal to the amount wrongfully withheld and reasonable attorney fees (§§ 5321.16(C)).
Lease, Rent & Fees:
- Rent Is Due: As stated in the lease.
- Rent Increase Notice: No statute.
- Rent Grace Period: No regulation.
- Late Fees: No statute, but case law allows limited late fees if specified in the lease. (See Ohiolandlordtenant.com’s “Landlord’s Corner – Late Fees in Ohio”) and (Ohiolandlordtenantblog.com’s “Amounts of Late Fees Allowed In Ohio Limited”)
- Prepaid Rent: No statute.
- Returned Check Fees: No more than $30 or 10 percent of the check amount, whichever is greater (§§ 1319.16).
- Tenant Allowed to Withhold Rent for Failure to Provide Essential Services (Water, Heat, etc.): Yes, but only under certain circumstances. Instead of paying rent to the landlord, the tenant may deposit rent with the court clerk with jurisdiction over the premises. Tenants must first notify the landlord in writing of the landlord’s failure to fulfill obligations defined in §§ 5321.04 or the rental agreement or if a governmental agency has found code violations that could affect health and safety. The landlord has failed to remedy the conditions in a reasonable amount of time considering their severity and the time necessary to fix, or within 30 days, whichever is sooner (§§ 5321.07, §§ 5321.08, §§ 5321.09 and §§ 5321.10).
- Tenant Allowed to Repair and Deduct Rent: No statute.
- Landlord or Tenant Allowed to Recover Court and Attorney Fees: Yes, but only allowed in certain circumstances. No provision regarding the payment of the landlord’s or Tenant’s attorney fees is permitted in any rental agreement (§§ 5321.13(C)). The landlord may recover actual damages and reasonable attorney fees for tenant violations of statutory Tenant Obligations §§ 5321.05(C)(1). Suppose the landlord fails to comply with the rules for returning the security deposit. In that case, tenants may recover money due along with damages equal to the amount wrongfully withheld, plus reasonable attorney fees (§§ 5321.16(C) and §§ 5321.04(B)).
- The landlord must make a reasonable attempt to mitigate damages to the lessee, including an effort to Rent: No statute.
- Abandonment/Early Termination Fee: No statute.
Notices and Entry:
- Notice to Terminate Tenancy – Fixed End Date in Lease: No notice is needed as the lease expires.
- Notice to Terminate Tenancy – Month-to-Month Lease: 30days’ notice (§§ 5321.17(B)).
- Notice to Terminate Tenancy – Week-to-Week Lease: Sevendays’ notice (§§ 5321.17(A)).
- Termination of Tenancy with 24 Hours Notice: No statute.
- Notice of Date/Time of Move-Out Inspection: No statute.
- Notice of Termination for Nonpayment: Three days’ written notice (§§ 1923.02) and (§§ 1923.04(A)).
- Termination for Lease Violation: Three days’ written notice (§§ 1923.02(A)(9)) and (§§ 1923.04(A)).
- Termination for Failure to Fulfill Tenant Obligations: 30 days’ written notice for violating any statutory tenant obligations affecting health and safety other than illegal drug-related activity. The notice must specify the date on which the rental agreement will terminate and the Tenant’s act or omission of noncompliance. Tenants can remedy the condition specified in the notice to avoid removing the rental agreement (§§ 5321.11).
- Termination for Drug-related Activity: Three days’ notice (§§ 5321.17(C)).
- Required Notice before Entry: Reasonable notice is required, with 24 hours being presumed to be reasonable, and entry is only allowed at reasonable times (§§ 5321.04).
- Entry Allowed with Notice for Maintenance and Repairs (non-emergency): Yes (§§ 5321.05(B)).
- Entry Allowed with Notice for Showings: Yes (§§ 5321.05(B)).
- Emergency Entry Allowed without Notice: Reasonable notice is not required in cases of emergency. (§§ 5321.04(8)).
- Entry Allowed During Tenant’s Extended Absence: No statute.
- Notice to Tenants for Pesticide Use: No statute.
- Lockouts Allowed: No (§§ 5321.15).
- Utility Shut-offs Allowed: No (§§ 5321.15).
Disclosures and Miscellaneous Notes:
- Name and Addresses: Written leases must include the name and address of the owner and the name and address of the owner’s agent. For oral rental agreements, this information must be provided to tenants in writing at the time of move-in (§§ 5321.18). Landlords must also file the name, address, and telephone number of the owner and that of the owner’s agent, along with the address and parcel number of the property, with the county auditor of the county in which the property is located (§§ 5323.02). Information filed with the county auditor becomes public information (§§ 5323.04). Failure to comply with the filing or updating of information requirements subjects the landlord to a fine of $50-$150 by the county auditor (§§ 5323.99).
- Copy of the Lease: No statute.
- Domestic Violence Situations: No statute. Statewide support resources include the Ohio Domestic Violence Network, the Ohio Family Violence Prevention Center and the Ohio Department of Rehabilitation and Correction, Office of Victim Services.
- Landlord Obligations: (§§ 5321.04)
- Compliance: Comply with all applicable building, housing, health, and safety codes;
- Repairs: Make all repairs and take all reasonable action to put and keep the premises in a fit and habitable condition;
- Common Areas: Keep all common areas of the premises safe and sanitary;
- Maintenance: Maintain in safe, working order all electrical, plumbing, sanitary, heating, ventilating, and air conditioning fixtures and appliances, and elevators
- Trash: For rental agreements that cover four or more units in the building, provide and maintain “appropriate receptacles” for the removal of normal garbage and waste and arrange for its removal.
- Water and Heat: Supply running water, reasonable hot water, and valuable heat between October 1 and May 1. This duty does not apply in cases where the unit is not required by law to be so equipped or if the unit is supplied with heat or hot water by an installation within the exclusive control of the Tenant and provided by a direct public utility connection.
- Landlord Access: Landlord must not abuse the right of access conferred by statute for inspection, repair or improvements or other reasons defined in Tenant Obligations to not withhold access to the premises.
- Prompt Eviction: Landlord must promptly start an eviction if the landlord has actual knowledge or reasonable cause to believe that the Tenant, any person in the Tenant’s household, or any person on the premises with the Tenant’s consent has been or is currently engaged in drug violations on the premises as defined in §§ 1923.02(A)(6)(a)(i), §§ 2925 and §§ 3719.
- Servicemembers Civil Relief Act: Comply with the rights of tenants under the federal Servicemembers Civil Relief Act, 117 Stat. 2835, 50 U.S.C. App. 501.
- Tenant Obligations: (§§ 5321.05)
- Compliance: Comply with all applicable state and local housing, health, and safety codes that impose requirements on tenants;
- Cleanliness: Keep that part of the premises that he occupies and uses safe and sanitary;
- Trash: Dispose of all garbage and waste in a clean, safe, and sanitary manner;
- Plumbing and Electrical: Keep all plumbing fixtures in the unit or used by the Tenant as clean as their condition permits, and use and operate all electrical and plumbing fixtures properly;
- Appliances: Maintain in good working order and condition any appliances supplied by the landlord and required to be maintained by the Tenant under the terms of a written lease;
- Damage and Defacement: Refrain from and forbid any person on the premises with the Tenant’s permission from destroying, defacing, damaging, or removing any part of the premises, fixtures, or appliances;
- Lawful Activity: Must not violate or allow drug-related activity as defined and prohibited in §§ 2925.01 and §§ 3719.01 or any similar municipal ordinance;
- Quiet Enjoyment: Must not disturb the peaceful enjoyment of the premises by neighbors;
- Reasonable Access: Must not unreasonably withhold consent for landlord to enter the unit for inspection, repair, alterations, or improvements, large parcel delivery too large for the Tenant’s mail facilities, supply of necessary or agreed services, or showing the unit to prospective or actual buyers, mortgagees, tenants, workmen or contractors.
- Retaliation: Landlord may not retaliate against a tenant by increasing rent, decreasing services, or bringing or threatening eviction because the Tenant has:
- complained to an appropriate governmental agency of a building, housing, health, or safety code violation;
- complained to the landlord of conditions that violate Landlord Obligations as defined in §§ 5321.05;
- Or joined with other tenants to negotiate or deal collectively with the landlord on any terms or conditions of a rental agreement.
- Tenant may use any retaliatory action by the landlord as a defense to an eviction, to recover possession of the premises or to terminate the rental agreement (§§ 5321.02).
- Lead Disclosure: Landlord must disclose all known lead paint hazards. Landlord must also provide tenants, as an attachment to a written lease, with an information pamphlet on lead-based paint hazards.
- Eviction of Tenant Allowing Sex or Child-victim Offender to Occupy Premises Near School: Landlord may terminate the rental agreement of a tenant who allows occupancy of the premises by any sex offender or child-victim offender prohibited from establishing residence within 1,000 feet of any school or child day-care center under §§ 2950.034 . However, if the landlord who is authorized to terminate such a tenancy does not do so, landlord is not liable for any injury, death, or loss to person or property that allegedly results from that decision (§§ 5321.051(2)).
Court Related:
- Ohio Small Claims Court
- Limits: $3,000 (§§ 1925.02(A)(1))
- Eviction Cases Allowed in Small Claims: No, eviction cases in Ohio are heard in county or municipal court or a court of common pleas. (§§ 1923.01(A))
- Ohio Small Claims Court – A Citizen’s Guide (PDF)
- Cleveland Municipal Court – How to File a Small Claim
- Muskingum County Court Guide to Small Claims Court
- Ohio Trial Courts (By County)
- Statute of Limitations
- Written Contracts: 8 years (§§ 2305.06)
- The Supreme Court of Ohio and the Ohio Judicial System
- Ohio Attorney General
- Ohio State Bar Association
- Legal Aid:
Business Licenses:
- Business License Required: No statewide statute, but local cities and counties may have regulations and requirements. Check with your local governing authority.
Helpful Links
State Agencies & Regulatory Bodies
Housing Authorities
- U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development – Ohio
- The Ohio Housing Finance Agency
- Ohio.gov — Housing
- Ohio Department of Insurance
- Ohio Guide to Homeowners Insurance (PDF)
- Ohio.gov – Consumer Protection
- Ohio Department Of Commerce – Real Estate Licensing
- Akron Metropolitan Housing Authority
- Allen Metropolitan Housing Authority
- Ashtabula Metropolitan Housing Authority
- Cincinnati Metropolitan Housing Authority
- Clermont Metropolitan Housing Authority
- Cleveland Housing Authority
- Columbus Metropolitan Housing Authority
- Cuyahoga Metropolitan Housing Authority
- Greene Metropolitan Housing Authority
- Lake Metropolitan Housing Authority
- Lucas Metropolitan Housing Authority
- Portage Metropolitan Housing Authority
- Stark Metropolitan Housing Authority
- The Hancock Metropolitan Housing Authority
- Trumbull Metropolitan Housing Authority
- Tuscarawas Metropolitan Housing Authority
Realtor, Landlord, and Tenant Organizations
- REALTORS® Associations
- Landlord Associations
- Ohio Landlord Association
- Lake Erie Landlord Association
- Columbus Apartment Association
- Northeast Ohio Apartment Association
- Greater Dayton Apartment Association
- Mahoning Valley Real Estate Investment Association
- Stark County Real Estate Investors Association
- Akron Canton Real Estate Investors Association
- Columbus Property Investors Association
- Real Estate Investors Association of Greater Cincinnati
- Tenant and Affordable Housing Organizations
