Landlords and tenants will face legal issues during the rental process, but not every case needs to involve the courts. This article will help you learn how the laws in your state handle everything from security deposits to termination notices so you can easily navigate these.
This article is not an exhaustive or a substitute for qualified legal advice. Laws and statutes are subject to change and may vary by county or city. You are responsible for performing your research and complying with all laws applicable to your unique situation.
We recommend consulting with the appropriate government agencies and a qualified lawyer if you have legal questions or concerns. Your state bar association may have a referral service to help you find a lawyer with experience in landlord-tenant law.
Official Rules and Regulations
- S.C. Code Ann. §§ 27-40 – Residential Landlord and Tenant Act
Security Deposit:
- Security Deposit Maximum: No statute.
- Security Deposit Interest: No regulation.
- Separate Security Deposit Bank Account: No rule.
- Pet Deposits: No rule.
- Non-Refundable Fees: No rule.
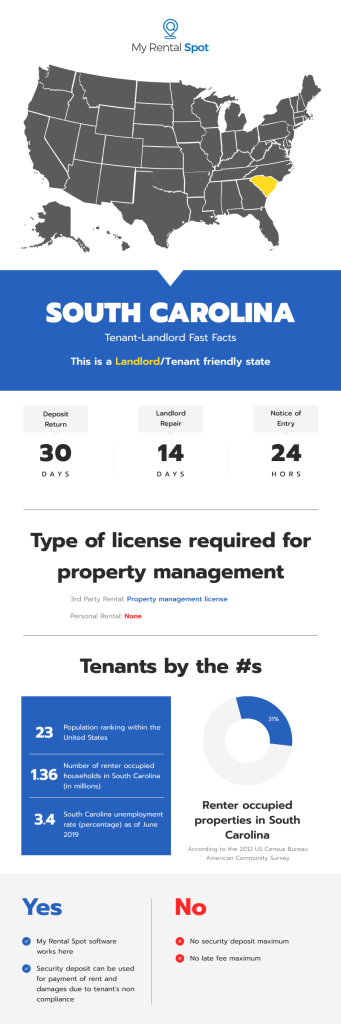
- Deadline for Returning Security Deposit: 30 days after termination of the tenancy and delivery of possession and demand by the tenant, whichever is later.
- The tenant shall provide the landlord in writing with a forwarding address or new address to which the written notice and amount due from the landlord may be sent.
- Suppose the tenant fails to provide the landlord with the forwarding or new address. In that case, the tenant is not entitled to damages under this subsection, provided the landlord (1) had no notice of the tenant’s whereabouts and (2) mailed the written notice and amount due, if any, to the tenant’s last known address (§ 27-40-410(a)).
- Permitted Uses of the Deposit: (§ 27-40-410(a))
- Unpaid rent and fees,
- Damages that the landlord has suffered because of the tenant’s noncompliance with Section §§ 27-40-510
- Require Written Description/Itemized List of Damages and Charges: Yes (§ 27-40-410(a))
- Disclosure of Deposit Calculations: If the landlord rents more than four adjoining units, the landlord must disclose the differing methods of calculating deposit amounts before signing the agreement. (§ 27-40-410(c))
- Failure to Comply: If the landlord fails to comply with § 27-40-410(a), the tenant may recover the property and money in an amount equal to three times the amount wrongfully withheld and reasonable attorney’s fees (§ 27-40-410(b)).
Lease, Rent & Fees:
- Rent Is Due: Rent is payable without demand or notice at the time and place agreed upon by the parties. Unless otherwise noted in writing, rent is due at the beginning of the month and payable at the dwelling unit (§ 27-40-310(c)).
- Rent Increase Notice: No statute.
- Rent Grace Period: No regulation.
- Late Fees: There is no statute, but late fees can be considered “rent” for collections (§ 27-40-210 (11)).
- Prepaid Rent: No statute.
- Application Fees: No rule.
- Returned Check Fees: $30 (§ 34-11-70).
- Tenant Allowed to Withhold Rent for Failure to Provide Essential Services (Water, Heat, etc.): Yes (§ 27-40-630(a)(1)) and (§ 27-40-640).
- Tenant Allowed to Repair and Deduct Rent: No (§ 27-40-630(c)).
- Landlord Allowed to Recover Court and Attorney Fees: Yes (§ 27-40-770(c) and § 27-40-750).
- Landlord Must Make a Reasonable Attempt to Mitigate Damages to Lessee, including an Attempt to Rerent: Yes (§ 27-40-730(c)).
- Abandonment:
- 15 Days after Default: The unexplained absence of a tenant from a dwelling unit for fifteen days after default in the payment of rent must be construed as abandonment of the dwelling unit. (§ 27-40-730(a)).
- Termination of Utilities: If the tenant has voluntarily terminated the utilities and there is an unexplained absence of a tenant after default in payment of rent, abandonment is considered immediate (§ 27-40-730(b)).
- Personal Property: If the tenant legitimately abandoned the unit, the landlord may enter the dwelling and dispose of personal property with a total value of less than $500. (§ 27-40-730(d)) The landlord cannot be liable for the disposal of property more than $500 unless the landlord was grossly negligent (§ 27-40-730(f))—also, review § 27-40-710(d).
Notices and Entry:
- Notice to Terminate Tenancy – Fixed End Date in Lease: No notice is needed as the lease expires. I recommend giving 60 days’ notice anyway.
- Notice to Terminate Tenancy – Month-to-Month Lease: 30 days (§ 27-40-770(b)).
- Notice to Terminate Tenancy – Week-to-Week Lease: 7 days (§ 27-40-770(a)).
- Notice of Date/Time of Move-Out Inspection: No statute.
- Notice of Termination of All Other Leases for Nonpayment:
- A 5-day notice can be written conspicuously in the lease so that termination can occur five days after the rent is not paid without additional information. Required verbiage for the lease provision can be found in § 27-40-710(b).
- If no such notice is written in the lease, then five days written notice is required before lease termination and filing for eviction.
- Access by the Landlord: Tenants shall not unreasonably withhold consent to the landlord to enter into the dwelling unit to inspect the premises, make necessary or agreed repairs, decorations, alterations, or improvements, supply necessary or agreed services, or exhibit the dwelling unit to prospective or actual purchasers, mortgagees, tenants, workmen, or contractors. (§ 27-40-530(a))
- Termination for Lease Violation: 14 days (§ 27-40-710(a))
- Required Notice before Entry: 24 hours notice and entry only at reasonable times (§ 27-40-530(c))
- Access Allowed with Notice for Maintenance and Repairs (non-emergency): Yes (§ 27-40-530(a)).
- Entry Allowed with Notice for Showings: Yes (§ 27-40-530(a)).
- Emergency Entry Allowed without Notice: Yes (§ 27-40-530(b)(1)).
- Entry Allowed During Tenant’s Extended Absence: No statute.
- Notice to Tenants for Pesticide Use: 24 hours (§ 27-40-530(b)(2)).
- Lockouts Allowed: No (§ 27-40-760).
- Utility Shut-offs Allowed: No (§ 27-40-760).
- Consequence of Self-Help Eviction: The tenant may recover possession or terminate the rental agreement and, in either case, recover an amount equal to three months’ periodic rent or twice the actual damages sustained by him, whichever is greater, and reasonable attorney’s fees. (§ 27-40-760)
Disclosures and Miscellaneous Notes:
- Name and Addresses: Landlords must disclose to the tenant in writing at or before the commencement of the tenancy the name and address of an owner of the premises or a person authorized to act on behalf of the owner as agent for purposes of service of process and receiving or receipting notices or demands (§ 27-40-420).
- Copy of the Lease: No statute.
- Domestic Violence Situations: No statute.
- Lock Changes: A tenant shall not change the locks on the dwelling unit without the landlord’s permission. (§ 27-40-530(e))
- Landlord’s Duties: (§ 27-40-440)
- Delivery: At the commencement of the term, a landlord shall deliver possession of the premises to the tenant in compliance with the rental agreement and Section 27-40-440. (§ 27-40-430)
- Compliance: Comply with the requirements of applicable building and housing codes materially affecting health and safety;
- Repairs: Make all repairs and do whatever is necessary to put and keep the premises in a fit and habitable condition;
- Common Areas: Keep all common areas of the premises in a clean and safe condition;
- Maintenance: Maintain in good and safe working order and condition all electrical, plumbing, sanitary, heating, ventilating, air-conditioning, and other facilities and appliances, including elevators, supplied or required to be supplied; and
- Heat and Water: Supply running water and reasonable amounts of hot water at all times and affordable heat except where the building that includes the dwelling unit is not required by law to be equipped for that purpose or the dwelling unit is so constructed that heat or hot water is generated by an installation within the exclusive control of the tenant and supplied by a direct public utility connection.
- Tenant’s Duties: (§ 27-40-510)
- Compliance: Comply with all obligations primarily imposed upon tenants by applicable provisions of building and housing codes materially affecting health and safety;
- Cleanliness: Keep the premises that the tenant occupies and uses as clean and safe as the condition of the premises permits;
- Trash: Dispose of all garbage and other waste cleanly and safely;
- Plumbing: Keep all plumbing fixtures in the dwelling unit or used by the tenant as clean as their condition permits;
- Appliances: Use reasonably all electrical, plumbing, sanitary, heating, ventilating, air-conditioning, and other facilities and appliances, including elevators in the premises;
- Lawful Activity: Not deliberately or negligently destroy, deface, damage, impair or remove any part of the premises or knowingly permit any person to do so; and
- Quiet Enjoyment: Conduct himself and require other persons on the premises with tenant consent to conduct themselves in a manner that will not disturb neighbors’ peaceful enjoyment of the premises.
- Retaliation: § 27-40-910 states that landlords must not terminate, increase rent, or refuse to renew a lease to a tenant (who is not in default) who has:
- complained to a governmental agency charged with responsibility for enforcement of a building or housing code of a violation applicable to the premises materially affecting health and safety or
- the tenant has complained to the landlord of a breach of §§ 27-40.
- Lead Disclosure: Landlords must disclose all known lead paint hazards. Landlords must also provide tenants, as an attachment to a written lease, with an information pamphlet on lead-based paint hazards.
Court Related:
- South Carolina Small Claims Court
- Limits: $7,500, except in disputes between landlords and tenants (source)
- Eviction Cases Allowed in Small Claims: Yes (source)
- Your Guide to Magistrate’s Court in South Carolina (PDF)
- South Carolina Magistrate’s Court
- Statute of Limitations
- Written Contracts: 3 years (§ 15-3-530)
- Oral Contracts: 3 years (§ 15-3-530)
- South Carolina Judicial Department
- South Carolina Attorney General
- South Carolina Bar
- Legal Aid:
Business Licenses:
- Business License Required: No statewide statute, but local cities and counties may have regulations and requirements. Check with your local governing authority.
Helpful Links
State Regulatory Bodies & Agencies
- U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development – South Carolina
- SC Housing (South Carolina’s housing finance authority)
- South Carolina Housing & Utility
- South Carolina Human Affairs Commission—Fair Housing Division
- South Carolina Department of Commerce–Community Development
- South Carolina Insurance Division
- South Carolina Consumer Guide to Homeowner and Tenant Insurance (PDF)
- South Carolina Department of Consumer Affairs
- South Carolina Real Estate Commission
Housing Authorities
- Charleston County Housing and Redevelopment Authority
- Columbia Housing Authority
- Greenville Housing Authority
- South Carolina Regional Housing Authority No. 1
- South Carolina Regional Housing Authority No. 3
- Spartanburg Housing Authority
Realtor, Landlord, and Tenant Organizations
- REALTORS® Associations
- Landlord Associations
- Tenant and Affordable Housing Organizations
